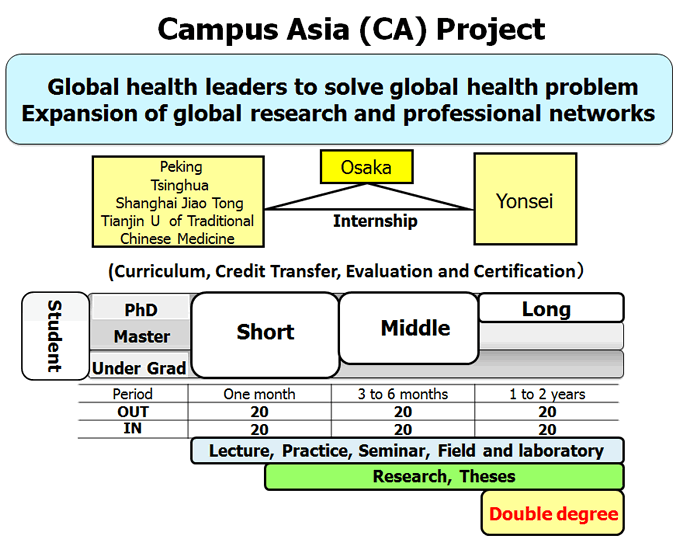
Objective
Raising research leaders in medicine and public health to solve global health problems due to non-communicable diseases, dementia and other age-related diseases through the Campus Asia Project among Japan, Korea and China. The mission of this program is to train undergraduate, master's and doctoral students to raise research leaders in the fields of medicine and public health. Students will obtain the sense of ethics and harmony, the comprehensiveness and flexible ways of thinking, as well as logical thinking. Students are also expected to establish fruitful networks which will enable them to work closely and efficiently with researchers and professionals in the future.
Background
Global aging has made a paradigm shift from communicable diseases to non-communicable diseases, dementia and other aged-related diseases in human. Asian countries, composing a large world population, boosted the global aging with declining birth rates. Rapid economic growth in the 1970's Japan, the 1990's Korea, and the 2000's China but recent stagnant raised the demand of reconstructing the system and policy for medical care and public health. Advanced research on prevention and medical care will be essential to provide evidence, skills and technology to solve the health problems of global aging. Japan has experienced a success in the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases (declines in both stroke and ischemic heart disease mortality) for which Osaka University has contributed substantially to conduct research and prevention programs. Korea and China have an increasing trend in ischemic heart disease mortality. Three countries are facing health problems due to dementia and other age-related diseases with rapid aging. The participant universities are strong for molecular and imaging researches on aging. Osaka University and Korea universities have conducted a large-scale population cohort studies on non-communicable diseases. Chinese universities have an advantage in performing research on Chinese medicines. The maximum use of advantage for the participating universities contributes to make the program successful.